Introduction:
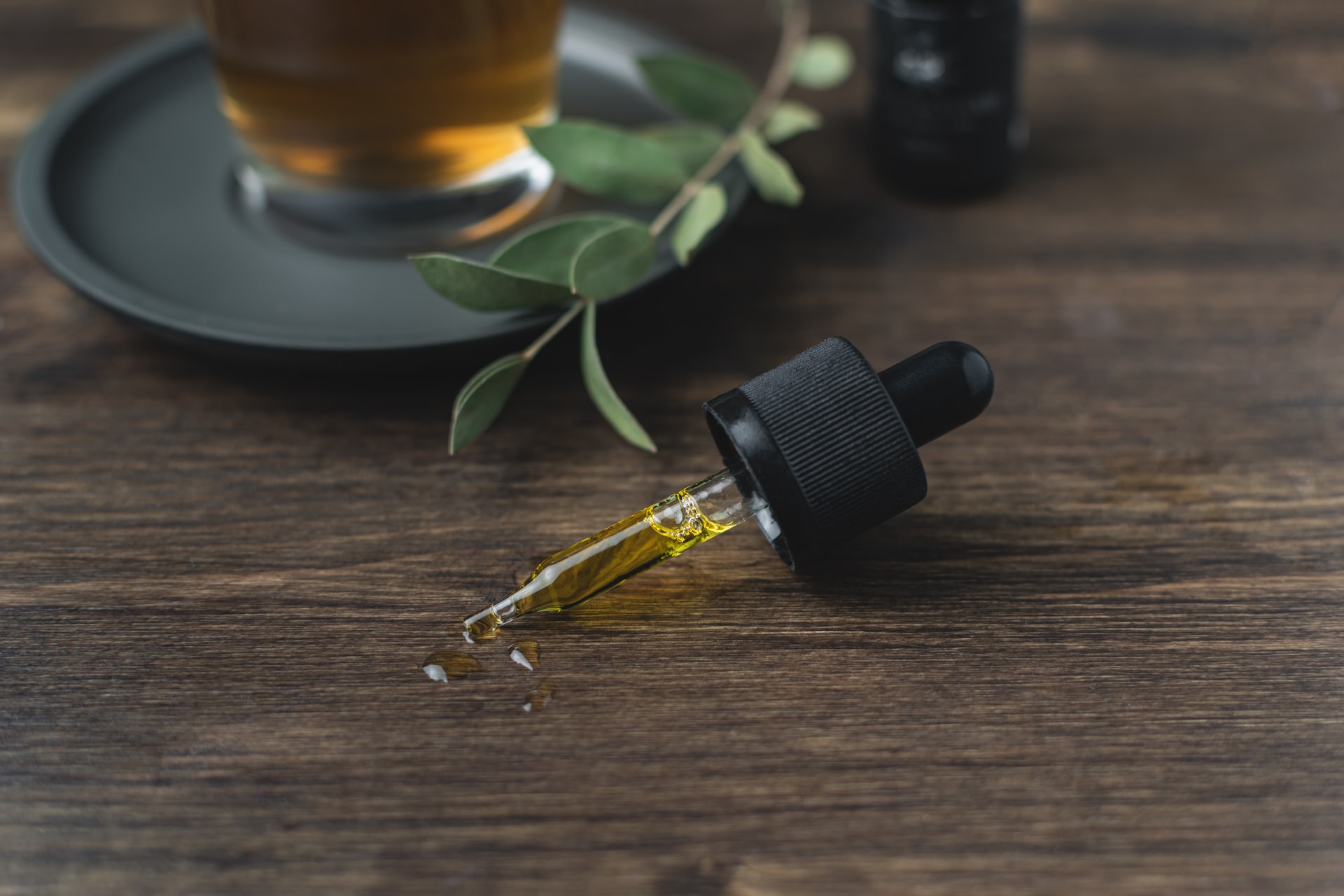
An essential oil is a chemical compound that is a concentrated form of a liquid which is hydrophobic in nature, or one that does not mix with water. These contain certain chemicals that are aromatic in nature, thus giving the essential oil and aromatic fragrance and are usually derived from plants.
Essential oils are also referred to as ethereal oils, aetherolea, volatile oils or are simply known by the name from which they are obtained or extracted, such as sandal wood oil obtained from the sandal wood plant.
The name essential oil is derived from the fact that the oil basically captures and contains the essence or smell or aroma or the fragrance of the plant from which it is prepared or derived and the same being characteristically different with each plant.
We need to differentiate the terms essential here from that used in biochemistry especially in the case of essential fatty acids or essential amino acids which provide nutrition and are required for building body muscle and tissue where as in this case, essential is only the property of the compound as has been explained above and there is no major biochemical use nor do these help in building body and muscle mass.
In order to obtain essential oils, the crude substances used must pass through a number of processes where in the oil is extracted using certain procedures such as distillation, cold pressing, extraction, filtration, tapping and sedimentation to name a few. These processes help obtain the finest grade and purest and most concentrated form of extract that can be obtained from the plant.
Essential oils find use in a variety of household products especially cosmetics where in they are used in soaps, shampoo and perfumes to name a few. They also find use in certain products used for religious procedures and rituals such as incense sticks. Lately, they have also been used to add and enhance the flavor of certain foods and are used widely in the food manufacturing industry.
History:
The use of essential oils in history finds mention around the year 1200 where in the process to obtain the same were believed to be used by Ibn al Baitar who was a pharmacist, physician and a chemist of Al Andalusian or Muslim controlled Spain which is modern day Spain as we know it.
These oils were used for a variety of illnesses ranging from a simple skin rash to complicated disease conditions during those days. The use of essential oils was considered as an alternative medicine therapy and many a times the same was given to either inhale or the body or the affected part was massaged with a specific oil so as to obtain relief. In some documented cases, the essential oil was dispensed to the patient in a bottle that they were supposed to carry and inhale at regular intervals, these bottles would come to be known as smelling bottles.
The use of essential and aromatic oils thus during the historical periods gave birth to what we now know as modern day Aroma therapy which forms an important branch of alternative medicine and is widely used even to date.
Processes used to obtain essential oils:
The mother or the crude plant substance has to go through a number of processes before the oil can be obtained and extracted.
Distillation is the commonest process where in the whole plant in the raw form is put into a machine called as a distillator which is put over water that is made to heat slowly. As a result, the steam passes over the plant carrying along with it small droplets of the volatile oils that the plant possesses, the same then condenses at the other end of the distillator from where the extract can be further concentrated and obtained.
This process is essential in obtaining oils such as eucalyptus, tea tree and lavender to name a few.
Expression is another process that was used earlier to distillation where in the peels of certain fruits and other substances were passed through a mechanically operated press where in the immense pressure applied would release the oils they contained.
This process was commonly used in cases of oils obtained from the citrus group such as orange and lemon.
Solvent Extraction is a process developed recently owing to the advances in biochemistry.
In this case, certain chemicals which act as solvents for the essential oils are used and the raw substances from which the oils have to be obtained are exposed to these solvents and then filtered. This solution is called as a concrete and is highly aromatic and concentrated in nature.
The concrete mixture is then exposed to a variety of other processes, cooling to name one where in it is cooled at extreme temperatures below negative and the various components are separated and thus obtained.
Substances commonly used are liquid carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol which are known to be good solvents.
Flora sol Extraction has been recently developed where in a chemical called flora sol is used which is also an extremely good solvent for essential oils. The advantage that this method possesses over others is that the oils are extracted at temperatures below that of the standard room temperature, thus the substances are not exposed to higher temperatures keeping the quality and standard of the obtained essential oil to the purest that can be made available.
Medical usage and pharmacology of essential oils:
The recent advances in the field of biochemistry and pharmacology we have been able to decipher and understand the action of various oils on the various systems of the body and how each plays a beneficial role to the body in its own unique way.
Oregano oil, for example contains carvacol which is known to control the growth of bacteria such as E. coli and bacillus cereus. It is known to act on their cell membranes thereby destroying the same thus controlling their growth and spread.
Similarly, thymol is another essential oil that is obtained from thyme and it is of immense medicinal use as it helps the spread of microbes in the body owing to its antimicrobial properties. It is also known to lower drug resistance especially to that of penicillin. There have been studies that have shown that these oils have cancer controlling properties and help check the spread and growth of the cancer in the body.
A certain number of oils, when taken orally or ingested have a beneficial action on the stomach as they enhance the secretion of gastric juice in the stomach which directly helps in improving and enhancing the digestive function of the stomach. Some of them also have beneficial properties lower down on the intestine as they help as anti-spasmodics and promote regular and healthy peristaltic movements essential to digestion of food and production of fecal matter.
Oils such as that obtained from Juniper have a beneficial action on the kidneys as they act as diuretics and promote the formation and expulsion of urine by the same.
A large group of oils are known to have soothing properties towards the skin and are applied locally in cases of certain skin conditions. The most famous of these is the tea tree oil that is an extract obtained from the tea tree.
As we have already mentioned above, essential oils also find use in aromatherapy, an alternative medical science used to treat certain disorders. Aromatherapy is used in cases of skin disorders, allergic reactions and is known to have a calming and soothing effect on the mind, thereby relaxing and calming the senses.
Side effects range from a minor skin reaction to liver dysfunction and the use of essential oils needs to be carried out carefully under supervision especially in those who suffer from allergies or have sensitive skin.
The oils also have varying temperatures of flammability. The most common of the lot are included and classified under the class 3 of flammable liquids as their flash point is between 50 to 60 degree centigrade. The oils classified under this include citrus, tea tree and lavender oil to name a few.
The use of certain oils should be restricted during pregnancy as they may lead from mild symptoms of nausea and vomiting to leading to an abortion as some of the oils contain abortive properties. Thus, their handling and use during pregnancy has to be under strict supervision.
Thus we can broadly understand how essential oils can be obtained, their uses and their pharmacological actions with their beneficial and harmful effects on the human body.
Further on, we shall study certain essential oils in greater detail and understand their uses and properties.
Bergamot Oil
Introduction
Bergamot derives its name from the plant Citrus bergamia Risso et Poiteau which belongs to the botanical family Rutaceae and the sub family Esperidea. The structure of the trees shows distinct big oval shaped leaves which are dark green in color and bare resemblance to that of the lime tree. The fruits are round and yellow and the flowers are white in color and shaped like a star.

Geographically, Bergamot is believed to be a native to the Italian region of Calibria apart from certain other European areas such as Greece and the Canary Islands from where it was believed to have been imported by noted explorer and historian Christopher Columbus.
Bergamot owes its derivation from the Spanish city of Berga situated in Calabria whereas its original cultivation had occurred and from where it was introduced to the rest of the world.
In the current scenario, this species is cultivated in many parts of the world, notably certain countries such as modern day Iran, Morocco, Greece, Brazil and Argentina to name a few.
Chemical contents of Bergamot
BEO is essentially made up of many molecules that are bio active, each having its own health benefits and thus has been deemed extremely useful and beneficial to the body.
In general, it contains a volatile or one that easily reacts with the external environment and a non volatile component. While the volatile component is around 95%, the non volatile comprises the remaining 5% of BEO.
The most important components that need to be mentioned here are citral, linalool and linalyl acetate which give the extract its distinct citrus flavor These three are essential and form an important component of BEO. Apart from these, there are also certain unstable compounds namely pinene and limonene which also add to the flavor but need to be removed owing to their unstable nature and their property to degrade easily. Thus, the removal of the unstable components helps enhance and improve the shelf life of this particular product.
Uses of Bergamot
Owing to its extremely fragrant smell and its useful components, bergamot finds its use in a variety of products ranging from medicinal preparations to cosmetics.
It is widely used in the perfume industry and the extract forms important components of perfumes, toiletries, soaps, shampoos, room fresheners etc owing to its ability of absorb and totally diminish unpleasant odors
It finds use as a flavoring agent in foods especially the cake industry and is widely used in preparations such as yogurts, cakes, puddings and other preparations.
Bergamot has been widely used by the Italians as a medicine from ancient times especially in cases of skin infections, respiratory problems, parasitic diseases, fevers and for female related disorders such as vaginal infections and leucorrhoea which is an abnormal vaginal discharge.
Its anti inflammatory properties have made it a valuable ingredient in certain preparations meant to be applied topically or locally to enhance and help with would healing and prevent any further infections.
It is also known to have a positive effect on the body as it inhibits the spread and growth of cancerous cells, thus research is underway to establish its use in treating cancers.
Bergamot is also known to have certain neuro protective properties as has been shown in recent studies and its property to decrease pain and also calm the mind are being studied.
Aroma therapy employs the use of bergamot essential oil as is it known to have a calming effect on the senses and is known to help cope with mood swings as it calms the same and also with sleep related issues as it has shown properties of helping induce the same. Thus it is also of immense help in the field of psychiatric disorders.
There have been certain cases of known adverse reactions especially that regards skin where in the oil has caused the outbreak of a severe rash or a dermatitis leading to itching and red eruptions on the skin.
Certain patients who suffer from hypersensitivity disorders have shown more severe forms of allergies such as that of respiratory problems which have been triggered by inhalation of the vapors of the oil.
Thus we can understand in detail how bergamot is extracted, its uses and its medicinal properties and how over the years it has become an essential part of not only the cosmetic industry but also the medical industry.
Lavender
Introduction
Lavender brings to our senses the pleasant sweet scent of an aromatic flower commonly used in fragrances, perfumes, room fresheners, toiletries and the flowers of which are used as components of a bouquet often gifted to people.

It is extremely interesting to know that the name of the plant Lavender originates from the word lavare from the Latin dictionary which directly translates into 'wash' because this plant was used very often in public baths as a means to cleanse and keep the body clean as well as purify the soul.
It was also used in the olden days and ancient times as meant to soothe and calm the body and the flowers of Lavender were used extensively for decorative purposes. It was believed to have had aphrodisiac properties and would be used by newly married couples as a means of improving the libido both in the male as well as the female owing to its soothing and calming effect on the mind.
Chemical components
Lavender oil is prepared by crushing the fresh flowers which secrete a sweet smelling and highly aromatic extract.
This extract has to pass through many processes so as to obtain the purest form of the lavender oil which can be made to put to use for various purposes.
Chemically, lavender oil consists of many various compounds, majority of them being extremely and highly volatile in nature.
The major components are namely linalyl acetate, cineole, linalool, nerol, borneol among others. The extract of the lavender plant is also rich in tannin's and flavinoids.
It is important to note here that these essential components are highly unstable and volatile in nature and thus the oil has to be extracted from freshly obtained leaves as they contain the highest amount of these components and the same diminish as the flower grows older and begins to wilt.
Uses
It is interesting to know that in earlier days, the pillows of those who would suffer from sleep disorders would be filled with lavender flowers owing to its aroma which would soothe and calm the mind and bring about a peaceful sleep to the person.
Commercially, lavender is available in various forms depending on the specific use.
It is available in the oil form, as a gel that can be used for bathing purposes, in soaps, tea and in the tincture form.
The field of alternative medicine also finds use of this component in various forms.
Aromatherapy promoted the use of Lavender oil where in the same is inhaled so as to obtain its beneficial soothing effects.
The oil is only meant to be inhaled and not ingested as the same can cause certain complications. The vapors from the oil can be inhaled directly or electrical devices are now available which can heat the oil at a slow temperature and spread the vapors across a wider space.
Herbal modes of medication also make use of the oil or add lavender to lotion or soap form which can be scrubbed or applied locally on the body to treat certain conditions.
The oil is also massaged so as to obtain its beneficial effects on the body.
Homoeopathy, another alternative mode makes used of Lavender in the tincture form where in the `essential oil is extracted using alcohol so as to obtain a mother tincture. This is either ingested or applied externally and is used for a range of symptoms ranging from a local skin infection or dermatitis to chronic cases of sleep disorders or insomnia.
Tea infused with Lavender is also available commonly and the same is consumed widely owing to its calming and soothing effects on the mind.
Lavender has been found to be useful in skin conditions especially dermatitis, eczema, allergic rashes and acne.
It use as an antiseptic and anti inflammatory has also been known and thus finds its use in lotions and creams applied on cuts, bruises and wounds.
Local application of lavender oil on the scalp has been found to nourish the same and help with stimulation and regrowth of hair follicles thus helping treat baldness, clinically known as alopecia.
Owing to its action on calming the central nervous system, it is recommended that Lavender not be taken along with certain conventional medication whose pharmacological action on the same has been well studied and documented. Thus is it advised that Lavender not be taken along with anti anxiety and sedatives such as morphine and its derivatives, diazepam, lorazepam and aplrazolam.
Thus is it essential to use the same under the supervision of a registered medical practitioner.
In certain cases, Lavender is known to have caused local irritation and rashes on the skin in those people who have known allergies or suffer from hyper sensitivity reactions.
Thus we can see how this aromatic flower has found its important place in our daily lifestyle both cosmetically and medically right from the early ancient times till date, the understanding of its components and uses only widening with the advances in modern biochemistry and pharmacology.
Peppermint
Introduction
Mentha piperita or mentha balsamea is commonly referred to as peppermint.
The current peppermint plant we know is actually a cross or a hybrid plant between a spearmint and water mint plant.

Originally, this plant was native to Europe but is now cultivated and is almost available all around the world.
Peppermint over the recent years has been extensively used in food and beverage preparations owing to its extremely distinct flavor and taste. Recently, with advances in pharmacology, there have been studies and extensive work has been done on ascertaining the medicinal properties of this plant.
In order to suit the taste buds and to enhance the flavors of peppermint, the plant has been crossed with other species so as to produce different flavors which have their own distinct characteristic and bring the same to the food or beverage they are added to.
Chemical constituents
The characteristic odor and taste on the peppermint plant is because of its high content of menthol which is responsible for the same.
Apart from menthol, the plant also contains traces of menthyl acetate, menthone, cineol and menthofuran as major components.
Other chemical constituents found in minor and smaller quantities are namely flavinoids such as hesperidin, eriocitrin and kaempferol along with certain terpenoids which also occur in smaller quantities.
Since peppermint grows extensively where ever it maybe planted, the oil has extremely high concentrations of pesticides used by the farmers which finally finds its way into the various water systems. Thus modern techniques of filtration and purification have to be applied so as to remove the same as they can have deleterious effects on the body.
Owing to this increased content of pesticide, it is known to help repel certain pests, especially insects such as mosquitoes and is used for better growth of plants in organic gardening.
Uses
Peppermint oil finds its use in the culinary as well as the medical world where in its use has been extensively researched and proven in a variety of conditions.
The culinary uses of peppermint include the use of its leaves which are often either consumed alone or added and mixed with other components and consumed.
Peppermint is also mixed with tea and is the same is widely consumed all over the world.
Dried peppermint leaves are used as a mouth freshener and also help enhance and improve oral and dental hygiene. The aroma from the menthol component also helps relieve bad breath.
More recently, peppermint finds its use in ice creams where in it a used as a flavoring agent, in fruit preserves, chocolates and candies, alcoholic beverages and products such as tooth paste.
Cosmetics also make use of peppermint as an agent especially certain soaps and shampoos and other products useful for skin care. Thus we see peppermint is now an important component of the cosmetic world and is widely used in the same.
The medicinal uses of peppermint primarily include its effectiveness in cases of irritable bowel syndrome where in it is known to be beneficial in treating the irregularities of the bowel and promoting peristalsis. Peppermint also has antibacterial properties and is used as a cholagogue and carminative.
It also has direct action on the lower sphincter or opening of the oesophagus and thus helps relieve symptoms of acidity and heart burn even though studies have not confirmed the same.
As an external agent used for applying locally, peppermint oil finds its use in relieving muscle and nerve pain as well as itching caused due to dermatitis.
Aromatherapy uses peppermint oil in cases of memory and alertness related issues as the inhalation of the vapors of the same are known to improve perception.
Peppermint is also used in Homoeopathy in the tincture form for cases of hyper acidity and irritable bowel syndrome. It is also useful in aborting acute episodes of cold and acute attacks of allergic rhinitis.
Fun fact
Q. Why does peppermint cause a sudden coldness especially in the nose and mouth when taken and why does the breath become icy cold after consuming a mint?
A. The menthol component of peppermint activates the cold sensitive receptors present on the mucosal and skin tissues thus giving a sense of extreme coldness to the food, air or water we consume immediately after eating a mint, hence the icy cool feeling!
This thus gives us a detailed explanation of peppermint, its biological and chemical understanding as well as its uses and why and how the mint causes its characteristic icy coldness!
Rosemary
Introduction
This is another invaluable contribution of the mint family and contains white needle like leaves which are extremely fragrant in nature. Rosemary or Rosmarinus officinalis belongs to the botanical family of Laminaceae and the botanical order of Lamiales.

The Mediterranean region is where it is natively found
Rosemary derives its name from the Latin dictionary from the words ros or dew and marinus or sea, thus the combination of the same culminates into rosemary or dew of the sea!
The Greek also refer to it as Anthos or flower and it is historically significant to them.
An ancient myth says that the Virgin Mary had spread her cloak over the white flowers of the rosemary plant while she was resting and the same flowers magically turned blue, thus the plant also came to be known as Rose of Mary and has ever since been considered sacred by the Greeks, Romans and the Egyptians.
Chemical Constituents
Rosemary oil is obtained from the leaves and flowers which are picked freshly and crushed. It has a very characteristic odor which is aromatic and sweet in nature. The same is used as an important component in various perfumes and other cosmetics.
Phytochemicals form a major component of the oil extract and the major components include camphor, rosmarinic acid, ursolic acid, betulinic acid, carnasol and carnosic acid.
Owing to the high concentration of camphor in the oil, it is highly volatile and inflammable and thus needs to be stored carefully. Also owing to the concentration of other adulterants the solution has to pass through many layers of filtration and micro filtration so as to remove the same and obtain the purest form of oil that can be made available.
Uses
Rosemary oil is now used as an essential component both in the culinary as well as medical field. Over the years, research and an understanding into its chemical components has given us a deeper understanding of its components and how the same act on various parts of the body.
Historically, the plant has always been considered sacred to the Europeans who use it for ceremonial as well as for worship and other purposes.
From the culinary point of view, the leaves of the rosemary plant are used commonly as ingredients especially in the Mediterranean cuisine owing to its astringent taste and its property of infusing the same aroma into food. The leaves are commonly added into non vegetarian dishes especially those that contain pork, turkey and chicken.
Rosemary leaves are also added to vegetable preparations and help enhance the flavor of the same.
In addition, the oil maybe added to charcoal used for purposes of roasting and barbecue to give the meat its distinct aroma.
Recent studies have shown that rosemary is extremely rich in omega 3 fatty acids and has an abundant quantity of the same, but apart from this, its has no other major nutritional benefit or value.
Cosmetically, rosemary oil is used in soaps, shampoo and other toiletries so as to enhance their aroma and also benefit the skin as it has a beneficial action on the same.
Rosemary also helps maintain healthy hair and promotes the regrowth of the same and thus the oil is also applied to the scalp and massaged to obtain better results in cases of hair fall and balding.
Medically, studies have shown that rosemary helps in improving the perception as it helps with clarity of mind.
It is also used in cases of coughs and colds and is known to help relieve headaches.
Studies have shown that it has a positive action on the nerves and helps with activating the cerebellar activity of the brain, thereby improving the capacity to learn and also improving memory.
Application of rosemary oil in females is known to help control vaginal infections and maintain the hygiene of the same.
A study in 2007 showed that rosemary was useful in building and improving the overall immunity of the body as it improved the antioxidant content of the blood within the body, thereby helping fight infections.
Rosemary oil also has the ability to help relieve pain and is used a a local application in cases of bruises and injuries. It is also used in baths and massages owing to the same properties.
The science of aromatherapy makes use of rosemary oil as the inhalation of the same is known to benefit and improve perception. It is also known to improve the grasping and perception power thus helping with learning and memorizing.
Thus rosemary is commonly used in this field of alternative medicine and its vapors are directly inhaled or the same is carried out using electrically operated devices that help vapourise the oil and spread over a larger area.
Tea mixed with rosemary is also widely available and is commonly consumed all over the world owing to its known health benefits.
Thus we can understand in detail the importance of the rosemary and how it has multiple uses both in the field of medicine as well as the culinary sciences.
Bitter Almond
Introduction
Bitter almond is a form of the common almond whose botanical name is prunus dulcis or prunus amygdalus.
The almond plant is native to the African and Indian subcontinent as well as some parts of the Middle East. The almond is the seed of this plant which is edible and is widely consumed as a dry fruit all over the world. The same is also used in many food preparations especially the Indian cuisine.

Almonds have been believed to have been the first plants to be domesticated and used for purposes of food.
The name almond, as we know it currently has been a derivation from other words that have come down through various vocabularies over thousands of years. The French used to refer it to as alemande or almande while the Latin called it amandula which was derivation from the Greek word amygdala.
The term amygdala or amygdaloid is commonly used to describe something that is shaped like an almond, and lies somewhere between an ellipse and a triangle.
The wild form of the almond plant, which has now been domesticated is known to have the chemical compound glycoside amygdalin as one of the components of its seeds, the same is released when the seed is crushed and it transforms into prussic acid which is chemically referred to as hydrogen cyanide which is extremely poisonous and can cause death if ingested.
Chemical Constituents
Chemically, bitter almond oil is composed of a variety of organic and chemical compounds. These also include certain enzymes such as emulsin which in the presence of water, reacts with the other chemical components such as amygdalin, glycosides and prunasin to form cyanide and glucose.
The bitter taste is mostly due to the presence of benzaldehyde which is almost always available and present in its purest form.
Bitter almonds also contain an extremely lethal and deadly concentration of hydrogen cyanide which can be present to the extent of roughly 10 milligram per almond. This dose can be lethal if consumed and thus the same has to be filtered and completely removed before the oil can be put for any use.
Uses
During earlier times, bitter almonds and the oil of the same was widely used for medicinal purposes but it was soon realized that the same was too dangerous to use as the mortality rate owing to poisoning was high.
As a result, most cultivators of almonds now use the sweet variety and the bitter variety has been banned or is grown under strict supervision so that the same cant be misused or put accidentally into the market without prior checking and the requisite filtering process.
Sweet almond oil has a number of cosmetic and medicinal uses and is used widely around the world for the same.
Almonds are also commonly used all over the world in food preparations and also yield almond milk which is very popular and consumed widely all over the world.
Bitter almond oil finds its medicinal use in cases of fever and in eliminating worms from the intestinal tract, especially tape worms.
It is known to have anti fungal, antibacterial and anesthetic properties.
Even though its medicinal properties are known, its application is to be carried out under supervision and it has been prohibited for internal use owing to its poisonous properties.
The use during in women who are pregnant or lactating has also been prohibited.
When consumed internally, as a milder side effect it may lead to vomiting and loose motions.
Thus we can understand and study the properties of the controversial bitter almond oil and how even though it has certain medicinal benefits, owing to its contents the same cant be extensively used or consumed by humans.
Herbs and Spices
Herbs
Introduction
Herbs in general can be classified as a set of plants that are used for purposes of food, medicine, and flavoring or for their unique aromatic properties.

Herbs primarily refer to those parts of the plants which are green, leafy and flowering and they are usually vary from spices as the latter are the products of other parts of the plant and are usually dried.
Herbs can also be referred to as herbaceous plants.
In recent years, owing to the advances in botany and our understanding of the chemical and medicinal properties, herbs have become an important part of both the culinary as well as the medical science and are widely used for the same all over the world.
Historical perspective
The earliest known recorded use of herbs is documented approximately around the period of 5000 BC during the Sumerian Empire.
Egyptian manuscripts have also shown that they commonly used herbs for both cooking as well as medicinal purposes. These specifically include the mention of coriander, fennel and thyme.
The Greeks were also known to have made good use of herbs especially as medicines and the great physician of the era Galen was known to make concoctions using the same by mixing upto 100 different herbs in one formulation.
Thus we see how herbs have been historically significant right from the ancient eras.
Uses of Herbs
Culinary herbs are those which can be differentiated from vegetables and spices as they are used in extremely small quantities to provide a particular taste or impart a particular flavor to the food.
These herbs are usually small plants which are shrubs and are found all through the year.
A few herbs used commonly for cooking purposes include coriander leaves and seeds, thyme, rosemary, lavender, basil and parsley.
Medicinal herbs find an important role and place in our medicinal sciences and have been used for the same for thousands of years.
The Chinese have been using herbs since the ancient times as a medicinal science and by mixing and consuming various herbs to obtain their health benefits and also treat certain disorders. The concept of Chinese herbal tea which involves the mixture of tea with various medicinal herbs is used till date and it helps treat a variety of disorders. A few herbs added to such tea's include lavender, rosemary, peppermint and chamomile, each having their own distinctive property and health benefit.
The Indian system of Ayurveda has also made use of herbs to treat various anomalies. They have been used as combinations which have to be ingested, applied or massaged in the form of oil on the affected part of the body so as to obtain relief. Ayurveda is a popularly used method of treatment and is widely used in India even today, even though its principles date back to thousands of years.
Religion also applies the use of herbs in certain rituals and practices thus deeming certain herbs as sacred. In India, herbs such as the tulsi or holy basil or Ocimum tenuiflorum, neem or Adazirachta indica, bael or Aegele marmelos and haldi or Curcuma longa are widely used in religious ceremonies and practices and are considered as extremely sacred plants.
The recent spread of Ayurveda and the advances in botany and microbiology have enabled us to understand better the properties of certain herbs. These are now thus mixed with certain other plants and are used in the preparation of cosmetics owing to their properties of helping clear the skin and improving its tone as well as their antiseptic properties and anti inflammatory properties.
Herbal cosmetics now include herbal face creams, lip sticks, body oils and fragrances.
Thus we get a brief understanding of herbs and how they are widely used for a variety of purposes.
Spices
Introduction
Spices are either a root, bark, fruit or seed of a plant that are used for either flavoring, preserving of bringing a certain color to food.

Spices maybe used wholly or maybe ground to form various combinations and added to food as a powder. Their main purpose is to add flavor to the food.
Spices are also known to have antimicrobial properties and are thus used more in warmer climates as they help prevent infectious diseases, specifically those spread through meat.
Apart from being used in foods, spices are also used as part of certain rituals, medical purposes and certain cosmetics like perfumes.
History of spices
The trading of spices is believed to have started around 2000 BC with pepper and cinnamon being the first to be exported to other parts of the world.
Spices were produced during this era along in the South East Asian region and the Mediterranean region.
Egyptians were also known to use spices for cooking as well as medicinal purposes. They were also made use of for the process of mummification and jars filled with various spices were discovered fro, intact tombs as they were believed to be an important aspect for the survival and well being of the departed soul in the afterlife.
By the year 1000BC, spices were widely used all over the world and could be easily found in the areas around modern day China, India as well as Korea. The South East Asian region was specifically known for exporting spices to other parts of the world especially the regions of Europe and the Americas.
The merchants from Indonesia were known to have traveled all around the globe including the regions of Africa, America and the Middle East for exporting spices.
This lead to certain sea routes being developed so as to facilitate the trading and the exchange of spices from one part of the world to the other. These sea routes came to be famously known as the spice routes and gave birth to port cities across the globe, including the Egyptian port city of Alexandria, the middle eastern port city of Beirut and the South African port city of Cape Town to name a few.
Thus we see how the ancient trade routes helped develop various cities all over the world and some of them went to become extremely important business and trading centers for countries even till today.
The Mesopotamian texts, the Indian Holy texts such as the Ramayana and the Romans have made definitive mentions of the use and the properties of the clove which was used extensively during those days.
Historically speaking and from the point of view of Religion and Religious texts, in regards to the story of the Genesis, the father of Jesus Christ, Joseph was also believed to have been sold as a slave by his own brothers to spice merchants and even in the Song of Solomon, a poem in the Bible, which is the Christian religious text, spices have been named and mentioned many a times.
Thus, the spice trade was the most famous and the most revered mode and route of business and spices were extremely expensive and considered as a commodity for the rich and privileged in the Western countries. The same continued till around the early 19th Century until the discovery of the new world and the Americas which then lead to the introduction of new flavors and spices such as vanilla, chilli peppers and chocolate.
Over the years, even though the production of spice has drastically increased, the quality of the same seems to have been compromised as the mixtures are now available in a powdered form and certain parts of roots, skin, bark and dried leaves are added to increase the quantity of the spice, thereby compromising and diluting its quality.
Spices can be available in various forms. Certain spices give a better flavor when used freshly as compared to those which can be dried or powdered and used later for cooking or other purposes.
Ginger, for example is best of use when obtained fresh as compared to a dried, stored form or powdered form of ginger.
Turmeric on the other hand is best made use of when it is obtained in the ground or the powdered form unlike the fresh form.
The advances in botany and our understanding of the medicinal and the culinary uses of spices have over the years lead to an increase in the use of various parts of the plants.
The seeds of certain plants are made use of as in the case of pepper, nutmeg, fennel and mustard.
Pepper of chilli is obtained from the fruit of the plant.
The barks of certain plants are used as spices as in the case of cassia and cinnamon.
Clove, a commonly used spice is the dried flower bud of a plant.
Saffron a spice used for its flavor especially in Indian cuisine is the stigma of the plant.
The most commonly used ingredients such as ginger and garlic are actually roots and have to be extracted from the soil.
Asafoetida, a flavoring agent is the resin or the extract from the plant.
Thus we see how we have evolved to use even the smallest and most delicate parts of the plant to obtain their flavors and make use of their benefits
Nutritionally, owing to their strong flavors, spices tend to add on to the calorific value of food. The ones made of or obtained from seeds contain more fats and carbohydrates and are the highest among the spices in regards their calorific value.
Certain spices are known to help with supplementing certain essential nutrients in the body as they are rich in both vitamins and minerals.
Paprika, for example contains a high quantity of vitamin A, approximately 1100 IU per tea spoon and is thus used to supplement the same.
Spices when consumed in large quantities also benefit the body as they supplement the same with certain essential minerals such as calcium, magnesium and iron to name a few.
Spices are also known to have a high content of phenolic compounds especially the flavinoids and are thus known for their anti oxidant properties.
Recent studies carried out on the medicinal and beneficial properties of fresh ginger and cumin concluded that the two have the highest anti oxidant properties and are extremely beneficial to the body.
This thus helps give an overview to spices and how they same have been as essential commodity from the point of view of trade and have gone on to become an essential part of our daily lives and also helping us through their beneficial medicinal properties.
We shall now understand the medicinal properties of certain spices in detail and explore the action of each on the body.
Burdock
Introduction
Burdock is commonly referred to as Arctium which comprises a genus of the biennial variety of plants.
Burdock belongs to the botanical family of Asteraceae, members of which find various uses for a many purposes all over the world.
It belongs to the botanical order of Asterales.

The plant grows widely all over the world and flowers between the months of July till October. The flowers of this plant are known to provide nectar for bees that produce honey.
The leaves are large are heart shaped.
The burdock plant consists of prickly heads which are known to easily latch onto clothing and fur and are known to have such strong clinging powers that it was recorded that birds that were caught or entangled into the same eventually found themselves trapped and died as they were not able to free themselves from the same.
The property of the burdock to cling was thus responsible for inventing the mechanism of the hook and loop fastener and also provided as an excellent mechanism for the dispersing of seeds.
Uses
Food and Drink
The burdock plant comprises of a tap root, the same is widely consumed and eaten as a root type of a vegetable.
This is extremely popular in the East Asian cuisine especially in China, Korea and Honk Kong.
The Chinese refer to this root preparation as niubang.
The Japanese consume the burdock root in a preparation knows as gobo.
The Koreans make use of the burdock root to prepare u-eong which is also referred to as tong e-eong or the whole burdock as it sold and consumed.
The roots can grow extremely long and penetrate deep into the soil and can measure as long a meter
It is extremely crisp and crunchy in its texture and its flavor comprises a mixture of pungent and sweet.
The stalks of the flowers are also used as food and have a taste similar to that of artichokes. The stalk is peeled and is either consumed raw or it is put into boiling water so as to soften it and then consumed.
The Japanese also consume the leaves of the plant, thus we see the whole plant is consumed for food purposes, leaving no part to waste whatsoever.
The advances in biochemistry enabled us to understand the nutrient and chemical value of the contents found in burdock. It was thus discovered that the root contains extremely generous quantities of potassium, amino acids and calcium which are extremely essential to the body.
The root also contains a compound called poly phenol oxidase which is responsible for imparting the characteristic brownish color
In Britain, burdock is one of the main ingredients of a soft drink that was widely consumed during the medieval ages. It was employed as a bittering agent in the manufacturing of beer.
Burdock also has the property to increase lactation in females and was thus used as a galactagogue.
Traditional Medicine
Since ancient times, burdock has been used for a variety of purposes and was believed to be a diuretic, a blood purifying agent and a diaphoretic.
Chinese traditional medicine has made use of the seeds since centuries owing to their medical benefits.
The extract of the burdock root, especially the burdock oil or bur oil as it is also referred to has also been used for ailments related to the scalp especially in Europe for centuries.
Recent studies have shown that bur oil is extremely rich in essential fatty acids and phytosterols.
Magical and mystical uses
In the region of Anatolia that lies in modern day Turkey, the burdock plant was believed to help ward off evil spirits and provide protection to the surroundings.
The women also weaved the same into kilims which were a type of a carpet or a rug that could be placed at home or the work place to ward off any evil spirits.
Side effects
The roots are naturally diuretic and thus should be avoided in case of dehydration. It efficacy in thus controlling blood pressure by helping in diuresis is still being studied.
The plant also contains a high amount of lactone and can cause allergies in those who are allergic to the same and thus should be avoided.
Owing to its actions on the uterus, pregnant women or those women wanting to become pregnant should not consume this plant as it may lead to an abortion or menstrual bleeding.
Burdock and fabric, an invention form a coincidence!
Around the year 1948, a Swiss inventor named George de Mestral became extremely curious after he walked his dog through a garden that had burdock and realized the seeds of the same had gotten stuck to his clothing as well as the dogs fur. He decided to observe the seeds under a microscope and thus discovered the discovered the hook and loop fastener mechanism used by the plant to disperse its seeds.
This hook and loop mechanism was eventually used to develop the fabric we now know as velcro which is used extensively in a variety of household items all over the world.
Thus we see that burdock to Mestral was what the apple was to Newton!
This thus explains in depth the uses of burdock and how the same is now used extensively all over the world owing to its various properties.
Coriander
Introduction
Coriander also referred to as cilantro or Chinese parsley is a herb which grows annually. All the parts of this plant are edible and are used extensively for culinary and medicinal purposes.
In India, this plant is commonly referred to as dhania and the whole plant including its leaves shoots and dried seeds are made use of.

Its Botanical name is Coriandrum Sativum and it belongs to the Botanical order of Apiales and the Botanical family of Apiaceae.
Coriander derives its name from the Latin word coriandrum which in turn finds its origins in the Greek term kopic koris that translates into a bed bug owing to its foul odor that resembles that similar to a bed bug.
It is also interesting to know that about half a liter of coriander mericarps were discovered within the tomb of the famous Egyptian King Tutenkhamun, thus showing the importance of coriander even during the ancient times.
Presently, coriander is grown almost all over the world including areas of America, Europe and South East Asia.
Uses
Coriander has many benefits and uses.
Its leaves are extremely rich in a variety of minerals as well as vitamins which include thiamine, vitamin C and vitamin B, namely riboflavin.
Amongst the minerals, it has a rich quantity of phosphorus, calcium, iron, sodium, oxalic acid and potassium.
Coriander also has rich stores of water, dietary fiber, carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
It has a small calorific value and thus is not extremely heavy on the body and can be easily digested,
Folk medicine has long used coriander for psychiatric disorders and mental issues especially to obtain relief in cases of anxiety and insomnia.
Coriander also has a diuretic property which has been made use of by the Indian traditional system of medicine and Ayurveda since the ancient times. In order to obtain the same effect, an equal amount of coriander seeds and cumin seeds is boiled in water which is then cooled, strained and consumed.
The plant is also known to help aid digestion and is used as a carminative agent.
Fresh coriander leaves contain a rich amount of vitamin A, Vitamin C and anti oxidants as well as phosphorus which are extremely beneficial for complaints of the eye especially macular degeneration, aging of the eye, conjunctivitis and help soothe the eye when stressed. The leaves are crushed and the juice is strained whose drops are put into the eyes to obtain relief.
Coriander also helps in treating certain inflammatory conditions such as conjunctivitis and iritis.
Coriander also helps in cases of epistaxis or nose bleed as it is known for its anti inflammatory properties and also helps improve and activate the clotting mechanism of the blood.
It also has an affinity for skin and skin disorders and helps treat the same. Coriander leaves have anti septic, anti fungal, detoxifying and dis disinfectant properties and the same are extremely helpful in treating skin disorders. It is just widely used locally in case of insect bites, dermatitis, rashes and hives.
Pregnant women have reported that nausea and vomits are controlled when they consume coriander, thus showing its benefit in treating the same and being helpful in cases of hyperemesis gravidarum.
The extract of coriander contains citronelol which is known for its anti septic properties. Additionally the other components also contain anti bacterial and anti fungal properties and are thus helpful in cases of diseases related to the mouth such as ulcers and bleeding gums.
Coriander also helps refresh the breath and thus finds use in cases of halitosis
Coriander leaves also contain generous amounts of fatty acids, namely oleic acid, lin oleic acid, stearic acid and palmitic acid and are thus known to act on the cholesterol levels on the blood and bring down the same.
It thus prevents the deposition of cholesterol on the arterial walls thereby preventing arteriosclerosis and reducing the risk of cardiac related issues especially myocardial infarct and neurological stroke.
There is a beneficial action on the digestive tract as it helps in improving the secretion of digestive and enzymatic juices of the stomach thereby improving the overall ability of the stomach to break down and digest food.
Thus we see how coriander has its own medicinal benefits and how the same can be made use of for not only cooking but for also for its other beneficial purposes.
Garlic
Introduction
Garlic is also referred to as Allium Sativum and belongs to the botanical order of Asparagales, botanical family of Amarylliadaceae and the botanical sub family of Allioideae.
Garlic is closely related to the onion and chive family and has been used extensively for purposes for flavoring and seasoning of food. It has been used as a food product right from the ancient Egyptian Era and continues to be used as the same till date.

Garlic grows almost all over the world and is a cultivated easily in almost every part of the globe.
The whole plant is used for a variety of culinary and medicinal purposes but the the bulb of the garlic or the pod which grows below the soil is most commonly used part.
Nutritionally, garlic is extremely rich and contains a variety of vitamins and minerals in abundance.
It also contains generous amounts of carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
Amongst the vitamins, major components include Vitamin B1 or thiamine, Vitamin B2 or riboflavin, Vitamin B3 or niacin, Vitamin B5 or pantothenic acid, Vitamin B6, folate and Vitamin C. Thus we see it is a store house of essential vitamins useful for body functioning.
Amongst the minerals, garlic is known to have generous quantities of calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium and zinc.
It also contains traces of selenium.
Biochemically, garlic is composed of sulphur related compounds and its derivatives such as allicin, poly sulphides, ajoene and certain enzymes, flavinoids and saponins.
The characteristic odor and taste that garlic gives off is primarily due to a reaction that occurs when the pod is broken or cut open which causes a spontaneous reaction leading to a breakdown of the sulphur and its related compounds.
Uses
Garlic has been used for a variety of purposes since the ancient times. Apart from being an important component of our food, it has also been used for its medicinal benefits as well as certain religious and spiritual purposes. We shall now glance in detail at each.
Culinary Uses
The bulb of the garlic is the most commonly used part in food and for cooking purposes. The bulbs are normally fleshy and divided into many sections that are individually referred to as cloves. It has a characteristically spicy and pungent odor and flavor that tends to sweeten as it begins to cook.
The garlic plant leaves as well as the flowers or bulbils which form a part of the head of the plant are also consumed in certain parts of the world although they have a milder flavor as compared to the garlic pod.
Often, garlic is added to butter so as to obtain a garlic flavored butter and is also added to certain breads to obtain garlic bread. These are widely consumed in many parts of the world especially in Asia and Europe. Garlic is also stored with vinegar and consumed in a pickled form. This also helps obtain garlic vinegar which is used for cooking purposes and to be added as a condiment or accompaniment with food.
Garlic is widely used for cooking purposes in the South East Asian region as well as in regions of Europe especially Italy, Spain and France whose cuisines very often use the same as a major ingredient for cooking.
Garlic is now also available in the powdered and the paste form which can be easily stored made use of later apart from the fresh form that is also widely available world over.
Historical Uses
The Chinese have been using garlic for their medicinal benefits since the ancient times. The Greek and the Romans used garlic as a remedy to relieve complaints coming on from the sun and was thus extensively used by them when on field during battles.
Hippocrates recommended its use for treating intestinal disorders as well as infectious diseases.
Garlic was also used in Egypt as means for invoking the deity while the emperors and rulers took their oaths.



